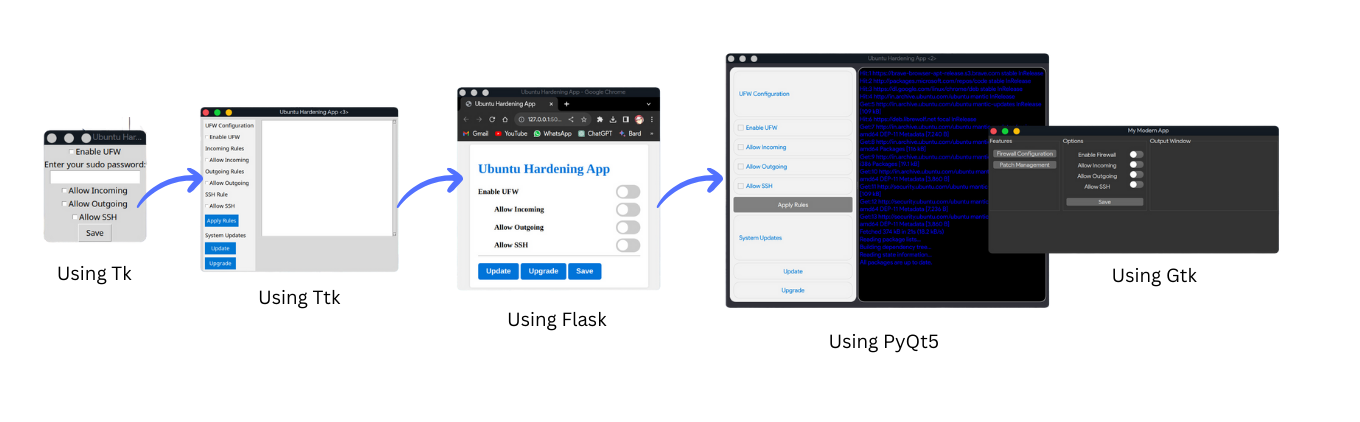
Enhance OS security through intuitive hardening procedures compliant with organizational policies, prioritizing user experience and interface
With features such as Patch Management,Port Protection,Firewall Configuration Management,SSH Hardening,Filesystem Permissions,Service Management,User and Group Management,Password Policies,Audit Logging,etc.
-
Patch Managemement: Keep the system up to date by applying security updates and patches regularly.
- Implemented with
aptpackage manager
- Implemented with
-
Firewall Configuration: Configure the firewall to restrict incoming and outgoing network traffic. Only allow necessary services and ports, and deny all others.
- Implemented with
ufwutility software
- Implemented with
-
SSH Hardening: To enhance SSH service security, disable root login, implement strong key-based authentication, limit login attempts, and if possible, disable password-based authentication for added protection.
- Implemented by modifying the SSH server configuration file (sshd_config).
-
Port Protection: Disables USB ports on a Linux system to prevent external devices from getting access.
- Implemented by creating a
udevrule file nameddisable-usb.rulesin the/etc/udev/rules.d/ directory. This rule disables all USB devices by setting their authorized attribute to 0.
- Implemented by creating a
-
Filesystem Permissions and Encryption: Review and set appropriate filesystem permissions to limit access to sensitive files and directories.Encrypt whichever file is required.
- Implemented by using the
chmodandchowncommand for permissions andgpu (GNU Privacy Guard)for encryption.
- Implemented by using the
-
Service Management: Disable unnecessary services and daemons to reduce the attack surface, to manage services and only enable those required for the system's operation.
- Implemented by using
systemctlcommand.
- Implemented by using
-
User and Group Management: Implement the principle of least privilege. Create separate user accounts for administrative tasks and regular usage.Remove or lock default and unused user accounts.
- Implemented with basic linux commands.
-
Password Policies: Enforce strong password policies using tools like Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM). Require complex passwords and set password expiration
- Implemented with
libpam-cracklibandlipam - pwqualityutility software
- Implemented with
-
Audit Logging: Enable and configure audit logging to monitor system activities and detect suspicious behavior.
- Implemented with
auditdutility software
- Implemented with
Patch Management simply updates all of the packages, removes orphaned packages and free up disk space.
User interacts with the GUI for Patch Management:
>>
Hit:1 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security InRelease
Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal InRelease [265 kB]
Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates InRelease [114 kB]
...
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
Calculating upgrade... Done
The following packages will be upgraded:
package1 package2 package3
...
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following packages will be REMOVED:
orphaned-package1 orphaned-package2
...
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 2 not upgraded.
All updates and cleanup completed.
Firewall Configuration is designed to configure a firewall according to your requirement.
User interacts with the GUI for Firewall Configuration:
>>
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following NEW packages will be installed:
ufw
0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 12 not upgraded.
Need to get 287 kB of archives.
...
...
Fetched 287 kB in 1s (477 kB/s)
Selecting previously unselected package ufw.
(Reading database ... 123456 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../ufw_0.36-7_all.deb ...
Unpacking ufw (0.36-7) ...
...
...
Setting up ufw (0.36-7) ...
...
Default incoming policy changed to 'deny'
Default outgoing policy changed to 'allow'
Rule added
Rule added (v6)
Rule updated
Rule updated (v6)
Firewall is active and enabled on system startup
SSH Hardening is designed to modify the SSH server configuration and enforce security settings by disabling root login and password-based authentication.
User interacts with the GUI for SSH Hardening:
>>
[Some informational output from sed commands, if any...]
/etc/ssh/sshd_config: 2 replacements made
Modified line: #PermitRootLogin yes
New line: PermitRootLogin no
Stopping sshd: [OK]
Starting sshd: [OK]
Port Protection is designed for disabling USB ports, prevent access to external hardware.
User interacts with the GUI for Port Protection:
>>>
USB port protection is now active.
USB ports are disabled.
Filesystem Permissions allows us to set limitations on who can read,write,execute a particular file and filesytem encryption encrypts a file for securing it.
User interacts with the GUI for File Permissions and Encryption:
>>>
Do you want to perform actions on a file in the current directory? (y/n):
>>>y
Files in the current directory:
file1.txt
file2.txt
file3.txt
Enter the filename:
>>>file1.txt
Do you want to (e)ncrypt or (c)hange permissions on the file? (e/c):
>>>e
File 'file1.txt' encrypted successfully.
#For change of permissions
>>>c
Enter the new file permissions:
>>>644
File permissions changed for 'file1.txt' to 644.
Service Management is designed such that services which are inactive for a certain time frame are disabled. User interacts with the GUI for Service Management:
>>>
Disabling <service_name> (Inactive for <days_since_activation> days)...
Disabling <another_service_name> (Inactive for <days_since_activation> days)...
...
Disabling <last_service_name> (Inactive for <days_since_activation> days)...
Service management complete.
User and Group Management is responsible for the several management tasks of differnet users and groups, such as such as creating user accounts, removing or locking default user accounts, and locking unused user accounts.
User interacts with the GUI for User and Group Management:
>>>
Creating administrative user account: adminuser
Changing password for user adminuser.
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: password updated successfully
Adding user `adminuser' to group `sudo' ...
Adding user adminuser to group sudo
Done.
Creating regular user account: regularuser
Changing password for user regularuser.
New password:
Retype new password:
passwd: password updated successfully
Removing default user account: guest
userdel: user 'guest' does not exist
Removing default user account: user1
userdel: user 'user1' does not exist
Removing default user account: user2
userdel: user 'user2' does not exist
Locking unused user account: unuseduser1
passwd: password expiry information changed.
Locking unused user account: unuseduser2
passwd: password expiry information changed.
Cleaning up temporary files
User and group management completed.
Password Policies is to enforce and manage strong password policies.
User interacts with the GUI :
>>>
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
libpam-pwquality is already the newest version (1.4.0-9ubuntu2).
libpam-cracklib is already the newest version (1.4.0-9ubuntu2).
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
minlen = 12
minclass = 3
maxrepeat = 2
maxsequence = 4
reject_username
enforce_for_root
Password policies have been configured.
Audit Logging is responsible for the detection of suspicious behaviour.A name.log file would be created which contains all the necessary audited records
>>>
Audit logging has been enabled and configured.
You can review audit logs in /var/log/audit/audit.log.
Example of a audit.log file :
type=SYSCALL msg=audit(1632717845.012:123): arch=c000003e syscall=2 success=yes exit=3 a0=7fffaa06eb3d a1=0 a2=1 a3=0 items=2 ppid=1234 pid=5678 auid=1000 uid=1000 gid=1000 euid=0 suid=0 fsuid=0 egid=1000 sgid=1000 fsgid=1000 tty=(none) ses=1 comm="open" exe="/usr/bin/cat" key="file_access"
type=CWD msg=audit(1632717845.012:123): cwd="/home/user/documents"
type=PATH msg=audit(1632717845.012:123): item=0 name="/etc/passwd" inode=12345 dev=08:01 mode=0100644 ouid=0 ogid=0 rdev=00:00 nametype=NORMAL cap_fp=0 cap_fi=0 cap_fe=0 cap_fver=0
type=PATH msg=audit(1632717845.012:123): item=1 name="/etc/shadow" inode=54321 dev=08:01 mode=0100400 ouid=0 ogid=0 rdev=00:00 nametype=NORMAL cap_fp=0 cap_fi=0 cap_fe=0 cap_fver=0