Java-ormen is an Object relation mapping library for REST API:s in Java. It is designed to build applications that are powered by a RESTful API instead of a database. This might be be useful when developing micro service oriented software.
The library's purpose is to allow Java applications to easily execute HTTP requests over an REST API. This will be achieved by create an abstraction on top of the REST calls, so the developer can invoke crud methods on Java POJOS.
Many ORM librarys restricts the user to do certain tasks (filtering etc etc). This api lets the user to write an own APIImplementation, so its possible to customize the library for different rest API:s. The library can talk with different rest api's with different behavior at the same time.
The library uses the Jackson ObjectMapper, so its possible to use jackson annotations to describe how objects shall be marshalled and unmarshalled. The JSONConverter are optional, and can be removed for something else, if needed ( its up to the APIImplementation ).
The library strives for creating immutable objects. This means that you can have control over your objects. But ofcourse, its impossible to make it immutable , if your code isn't.
One just simply do the following:
define your model. Remember to use the resourceUrl annotation to specify the endpoint for the dog model. We need a default constructor for jackson json reflection. Observe that we give the DogModel an Finder. It will give the model powers to retrive all dogs,with an static invocation from the code.
@ResourceUrl(url = "dogs")
public class DogModel extends Model {
private String name;
private int age;
public DogModel(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
DogModel() {
this.name ="";
this.age = 0;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
// override this method. You will return the identifying value for a specific model here. ( id or something like that )
@Override
public String getIdentifierValue() {
return name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public static final Finder find = new Finder(DogModel.class);
}
The good part with this model is that we will not need to write any marshall or unmarshalling logic. This is handled behind the sceens. But if you get into trouble you can use jackson json annotations on your fields. For example there might be times when you want to exclude some data from de json marshalling, or perhaps rename some data.
So now we have created a model. Its now time to use it to fetch data. Simply do the following.
apiConfig = new ApiConfig.ConfigBuilder().apiLocation("api").port("8081").host("localhost").build();
DogModel model = new DogModel("pluto",4);
DogModel modelWhenSaved = (DogModel) model.save();
// or why not try to delete a dog
model.delete();
// or fetch
fetchedModel = model.fetch();
// or update
updatedModelFromBackend = model.update();
// why not fetch all dogs?
List<Model> listOfDogs = DogModel.find.all();
In the code above, the dog model will call the rest api when the fetch method is invoked. A Dog is returned when data is expected to change.
Sure, no problem! Contributions are welcome!
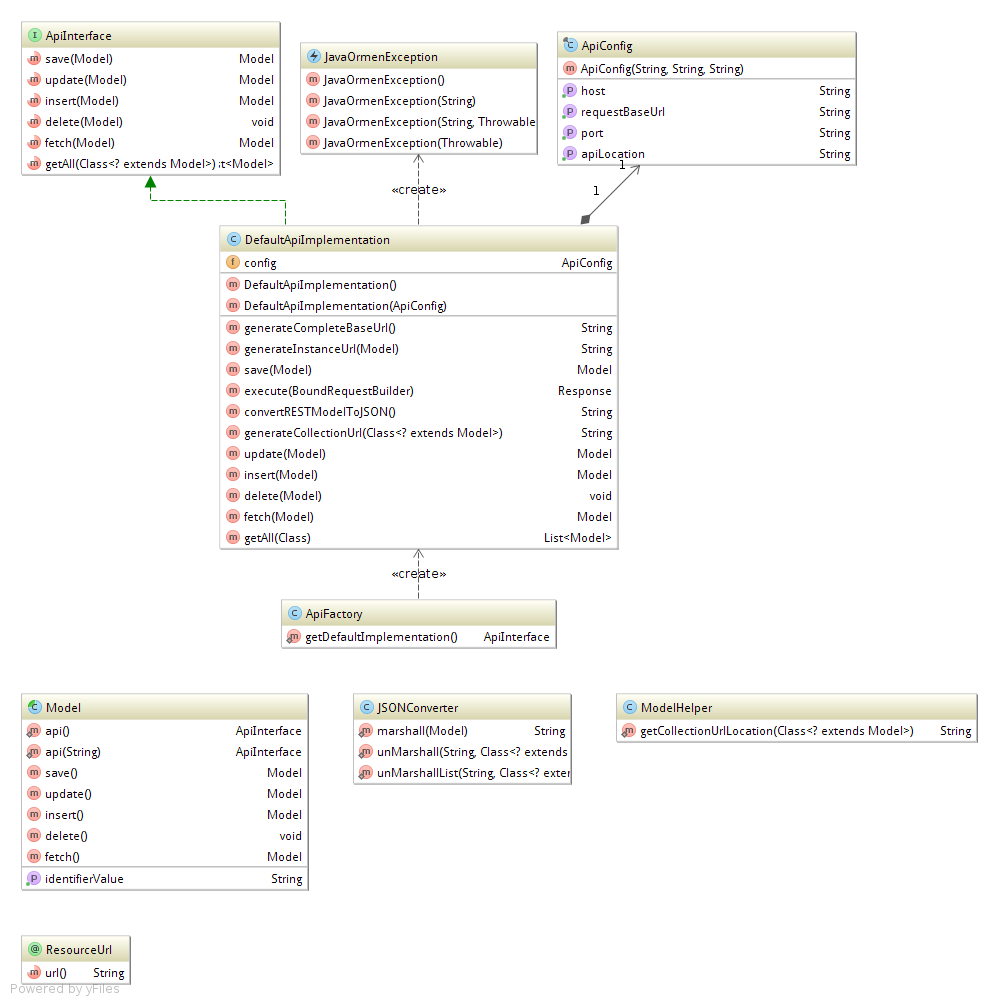
The library is very lightweight and only consists of a few classes, displayed here.
The MIT License (MIT)